Data switches are essential components in networking that facilitate the transfer of data between devices within a network. There are various types of data switches, each designed for specific purposes and network requirements. Here are the primary types:
1. Unmanaged Switches
- Description: Basic plug-and-play switches with no configuration required.
- Use Case: Small networks or home offices where minimal configuration is needed.
- Features: Simple, cost-effective, no management interface.
2. Managed Switches
- Description: Switches that offer advanced features and can be configured and managed.
- Use Case: Larger or more complex networks that require fine control over traffic.
- Features: VLANs, QoS, SNMP monitoring, redundancy features (like STP).
3. Smart Switches (Web-Managed or Partially Managed)
- Description: A middle ground between unmanaged and fully managed switches, offering some configuration options via a web interface.
- Use Case: Medium-sized businesses needing some level of management without the complexity of fully managed switches.
- Features: Limited VLAN, QoS settings, some monitoring capabilities.
4. Layer 2 Switches
- Description: Operate at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, using MAC addresses to forward data.
- Use Case: Basic LAN switching within a single network segment.
- Features: Efficient at switching data frames within the same network.
5. Layer 3 Switches
- Description: Operate at the Network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model, capable of routing based on IP addresses.
- Use Case: Larger networks that require both switching and routing functionalities.
- Features: Combines features of a switch and a router, supports routing protocols, VLANs, and inter-VLAN routing.
6. PoE (Power over Ethernet) Switches
- Description: Provide electrical power to connected devices over the Ethernet cables.
- Use Case: Networks with devices like IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points.
- Features: Simplifies the deployment of powered devices, reducing the need for additional power cables.
7. Stackable Switches
- Description: Switches that can be interconnected to function as a single switch, simplifying management and expanding capacity.
- Use Case: Growing networks requiring scalability and simplified management.
- Features: Stackability, redundancy, single management interface for the stack.
8. Modular Switches
- Description: Switches with slots that can accept different modules, allowing customization and scalability.
- Use Case: Large enterprises with diverse networking needs and future growth considerations.
- Features: High flexibility, modularity, supports various interfaces and functionalities.
9. Industrial Switches
- Description: Robust switches designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
- Use Case: Industrial environments like manufacturing plants, outdoor installations, and other extreme conditions.
- Features: Rugged design, extended temperature ranges, resistance to dust and moisture.
10. Data Center Switches
- Description: High-performance switches designed for data center environments.
- Use Case: Data centers needing high throughput, low latency, and advanced features.
- Features: High port density, support for high-speed interfaces (10GbE, 40GbE, 100GbE), low latency, redundancy.
11. Optical Switches
- Description: Use optical fibers for data transmission, often in backbone networks.
- Use Case: High-speed and long-distance data transmission.
- Features: High bandwidth, low latency, suitable for backbone and metropolitan area networks (MANs).
12. Virtual Switches
- Description: Software-based switches that operate within a virtualized environment.
- Use Case: Virtualized data centers and cloud environments.
- Features: Virtual machine networking, integration with hypervisors, scalability.
Comments (0)
Categories
Recent posts

Data switches
9 Jun 2024
ادارة المشاريع ...
29 Sep 2024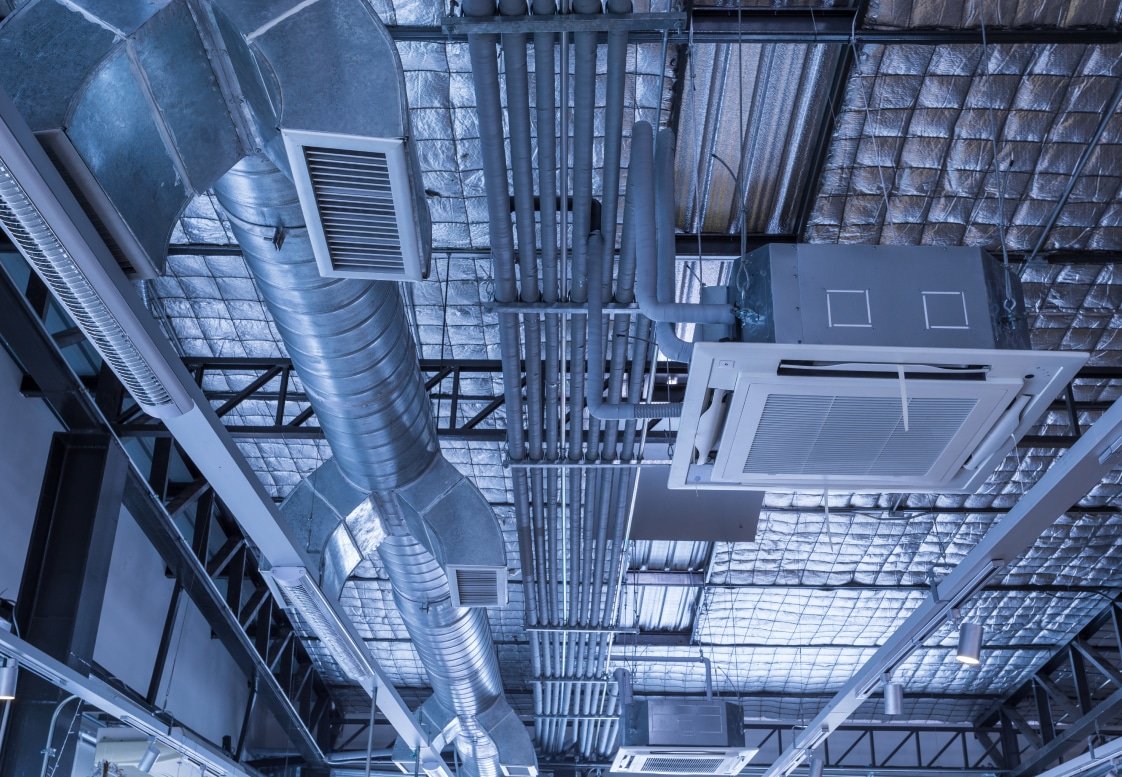
HVAC system
28 Sep 2024



